Knee Replacement
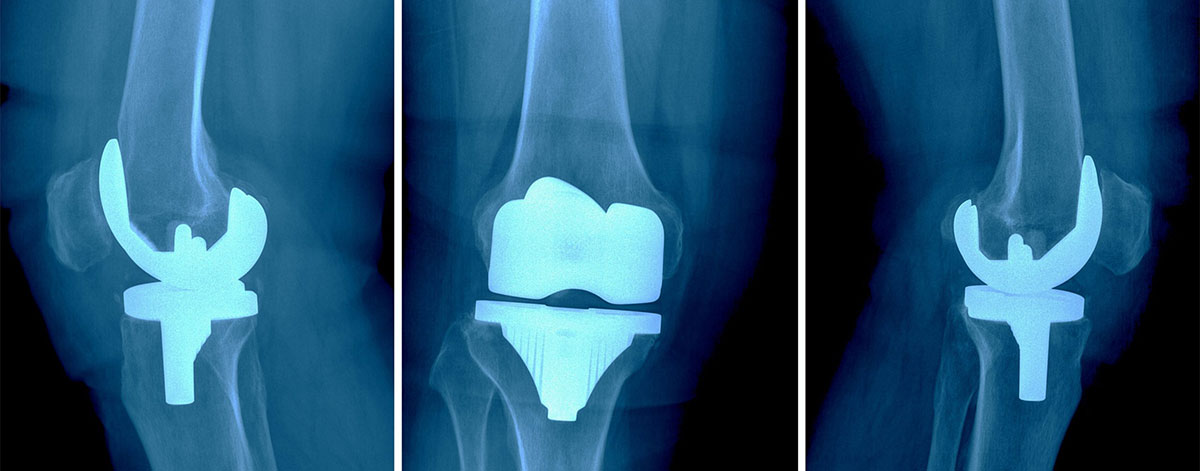
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or severely worn-out knee joint with an artificial prosthesis. The most common reason for knee replacement is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects the knee's cartilage and leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Other conditions that may necessitate knee replacement include rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, and certain knee injuries.
During the knee replacement surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged portions of the knee joint, including the ends of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone), as well as any damaged cartilage in between. These are replaced with artificial components made of metal, plastic, or a combination of both. The prosthetic components are designed to replicate the natural movement and function of a healthy knee joint.
There are two main types of knee replacement surgeries:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): In a total knee replacement, all three compartments of the knee joint are replaced - the medial compartment, lateral compartment, and patellofemoral compartment.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): If the damage is limited to only one compartment of the knee joint, a partial knee replacement may be performed, where only the damaged compartment is replaced.
Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended when non-surgical treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, and assistive devices, no longer provide adequate relief from knee pain and dysfunction.
Recovery from knee replacement surgery involves a period of rehabilitation and physical therapy to help restore strength, flexibility, and mobility. Patients are often encouraged to walk with the help of crutches or a walker initially and gradually transition to walking unaided.
Knee replacement surgeries have become quite common and are generally considered safe and effective for improving the quality of life for individuals with severe knee joint problems. However, as with any major surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with knee replacement, such as infection, blood clots, implant loosening, and nerve or blood vessel damage. Patients should thoroughly discuss the benefits and risks with their orthopedic surgeon before deciding to undergo knee replacement surgery.
